Understanding Modern Backend Architecture with Laravel and Queues
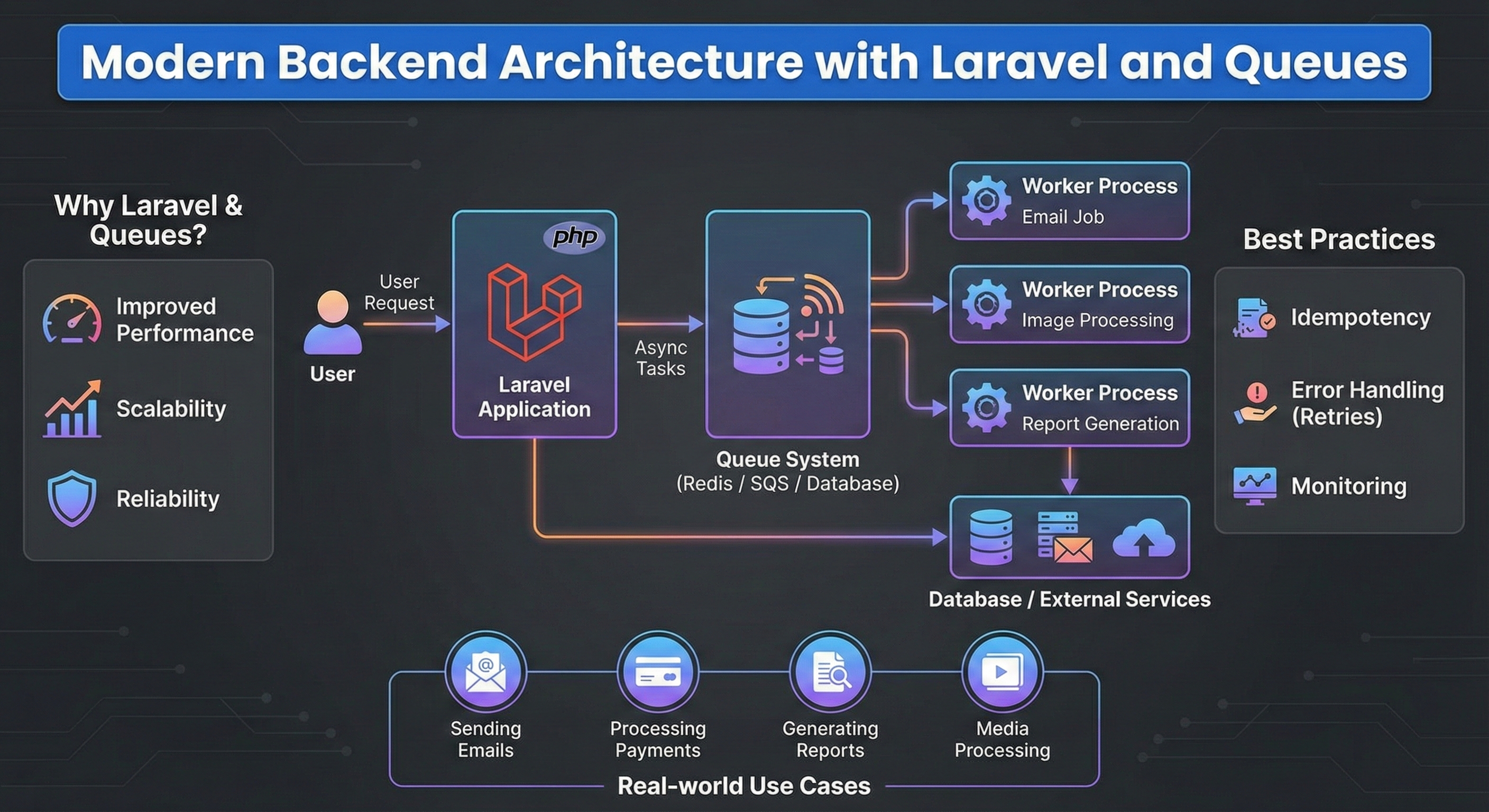
Modern backend development demands scalable, maintainable, and efficient systems. Laravel, a popular PHP framework, combined with queue mechanisms, provides developers with tools to build robust backend architectures that can handle asynchronous tasks effectively.
Why Laravel for Backend Development
Laravel offers elegant syntax, built-in features, and a strong ecosystem. It supports MVC architecture, making code organized and easy to maintain. Laravel also provides native support for queues, events, and jobs which are essential for modern backend systems.
What Are Queues and Why Use Them
Queues allow you to defer time-consuming tasks from the main request cycle. Instead of making users wait for tasks like sending emails or processing images, queues handle these operations asynchronously. This improves response time and user experience.
Benefits of Using Queues
- Improved Performance: Offloads heavy tasks from user requests.
- Scalability: Easily manage workload spikes.
- Reliability: Tasks can be retried on failure.
Laravel Queues Overview
Laravel supports multiple queue drivers including database, Redis, Amazon SQS, and more. This flexibility allows integration with various systems based on project needs.
Basic Queue Workflow in Laravel
- Job Creation: Define a job class representing the task.
- Dispatching: Push the job to the queue.
- Processing: Queue workers process jobs asynchronously.
Implementing Queues in Laravel
Setting Up the Queue Driver
Configure the queue driver in config/queue.php. For example, Redis is a popular choice for performance.
Creating a Job
Use the artisan command:
php artisan make:job ProcessOrder
Define the task logic inside the handle method.
Dispatching Jobs
Dispatch jobs from controllers or services:
ProcessOrder::dispatch($orderData);
Running the Worker
Run the queue worker to process jobs:
php artisan queue:work
Best Practices for Queue Usage
- Idempotency: Ensure jobs can run multiple times without side effects.
- Error Handling: Implement retries and failure handling.
- Monitoring: Use tools to monitor queue health and job statuses.
- Prioritization: Use multiple queues for different priority tasks.
Real-world Use Cases
- Sending notification emails
- Processing payments
- Generating reports
- Image or video processing
Combining Queues with Event-Driven Architecture
Laravel events can trigger jobs to run asynchronously. This approach decouples components and enhances system flexibility.
Conclusion
Using Laravel with queues enables developers to build modern backend systems that are responsive and scalable. This architecture pattern handles complex workflows without blocking user interactions.
Try Meetfolio for Your Personal Business Needs
If you need an easy way to create personal business card pages or set up booking calendars, check out Meetfolio. It simplifies online presence management and scheduling. Visit https://meetfolio.app to get started today.
Need a personal business card page or booking calendar? Meetfolio makes setup easy and fast. Visit https://meetfolio.app to get started.
Tech Insight
Tech Enthusiast & Writer
